Summary
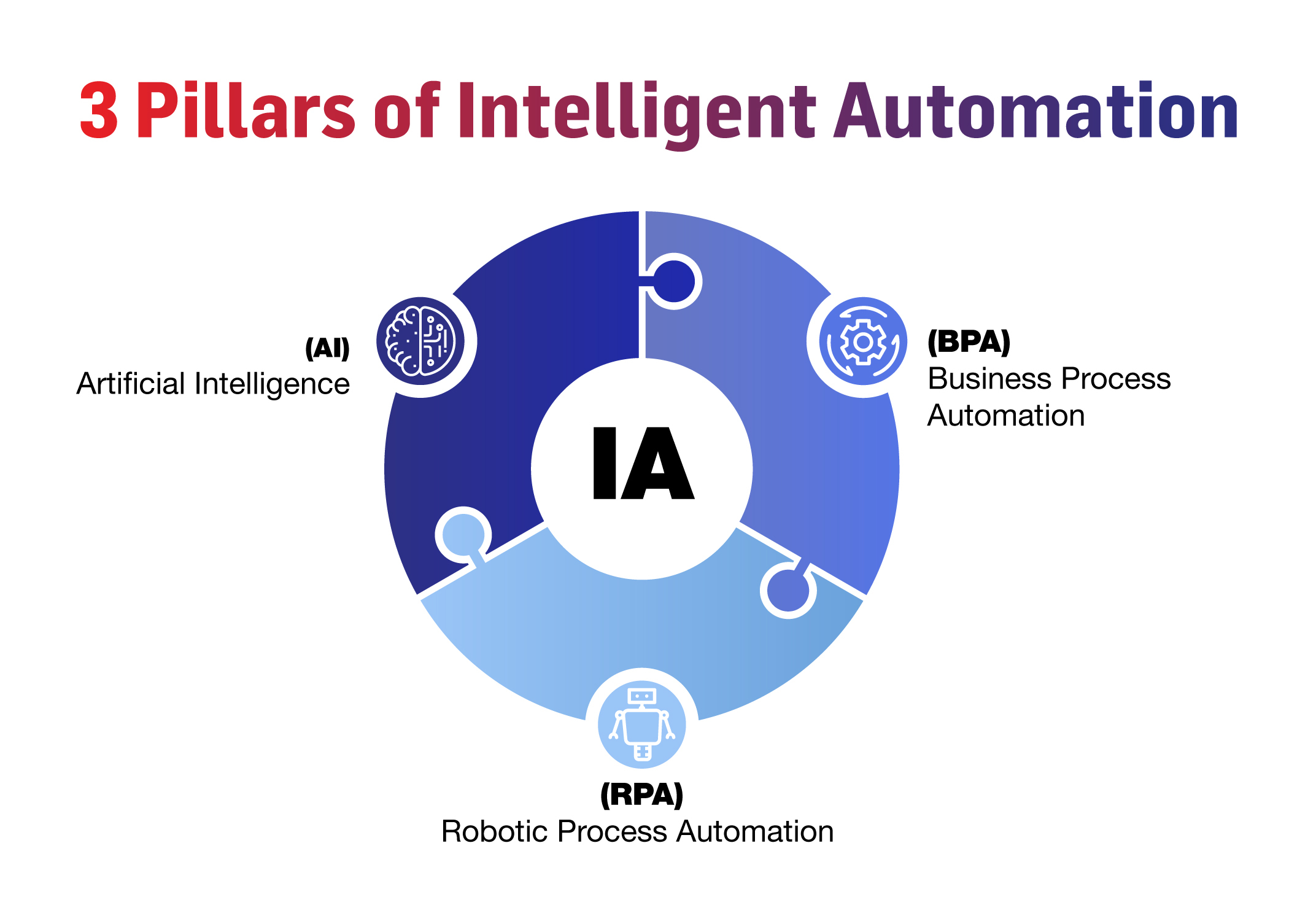
Intelligent Automation is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to create automated solutions that can learn, adapt and perform tasks that would otherwise require human intervention. It combines the cognitive capabilities of AI with the automation capabilities of RPA to deliver efficient and effective results. Intelligent Automation is designed to streamline workflows, reduce errors and improve productivity, by enabling machines to take on repetitive and time-consuming tasks, while humans focus on more complex and strategic activities.
Intelligent Automation has a wide range of applications across different industries, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail. It can be used to automate tasks such as data entry, customer service, and accounting, as well as to enhance decision-making processes through data analysis and predictive modeling.
One of the main benefits of Intelligent Automation is its ability to improve the speed and accuracy of business processes. By automating routine tasks, organizations can reduce processing times, eliminate errors, and increase efficiency. In addition, Intelligent Automation can help businesses to reduce costs by reducing the need for human labor and increasing output.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to Intelligent Automation. One concern is the potential for job displacement, as machines take on tasks that were previously performed by humans. Another concern is the potential for bias and errors in AI algorithms, which can result in incorrect decisions and actions. Additionally, there are challenges associated with integrating Intelligent Automation into existing systems and processes, as well as with ensuring data privacy and security.
Pros
- Increased efficiency: Intelligent automation can automate repetitive, manual tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more complex and strategic work.
- Improved accuracy: Automation can significantly reduce the likelihood of human error, leading to increased accuracy and fewer mistakes.
- Cost savings: Automation can reduce labor costs and operational expenses, resulting in significant cost savings for businesses.
- Faster processing: Automated systems can process data and complete tasks much faster than humans, resulting in quicker turnaround times for business operations.
- Scalability: Automated systems can be scaled up or down quickly, making it easy for businesses to adjust to changes in demand.
Cons
- High upfront costs: Implementing intelligent automation can be expensive, requiring significant investment in hardware, software, and training.
- Complex implementation: The implementation of intelligent automation can be complex, requiring significant planning and preparation to ensure that the automation process is seamless.
- Potential job loss: As automation replaces manual labor, some employees may lose their jobs or need to be reskilled for new roles.
- Security concerns: Automated systems can be vulnerable to security breaches and hacking, posing a risk to sensitive business information.
- Reliance on technology: Overreliance on automation can be problematic if systems fail or malfunction, potentially leading to significant disruptions in business operations.